The Importance of Equipment Calibration in Maintaining Data Integrity
Image by Unsplash.
New data-collection technologies, like internet of things (IoT) sensors, enable businesses across industries to collect accurate, minute-to-minute data that they can use to improve business processes and drive decision-making.
However, as data becomes more central to business processes and as more and more data is collected, collection errors become both more possible and more costly.
Here is why equipment calibration is key in maintaining data integrity — in every industry.
Bad Calibration, Bad Data
If a sensor or piece of equipment is improperly calibrated, the data it records could be incomplete, inaccurate or totally incorrect. This misinformation could be detrimental for businesses that integrate data-driven policies and strategies, as they rely on complete, up-to-date and accurate data.
In fact, poor calibration cost manufacturers an average of $1.7 million every year, according to a 2008 survey.
Poorly calibrated sensors and testing equipment can also present risks for consumers — which is why some industries control calibration. In medicine, for example, the FDA regulates equipment calibration. Medical manufacturers must regularly inspect and test monitoring equipment. Effective measuring and test equipment are vital for producing batches of drugs that are useful and safe for patient health.
Bad calibration can even lead to machine failure in businesses that rely on predictive maintenance, which is the use of IoT sensors to collect machine data that can help analysts predict machine failure before it happens. If a business’ data scientists are working with bad information, they are less likely to realize a particular machine or robot is failing. As a result, they won’t intervene with a repair until failure has occurred — a costly error that can effectively shut down some workflows.
Worse, if a business has come to depend on predictive maintenance, it may be caught off-guard by that machine’s failure — even more than if the same company relied on traditional maintenance strategies, rather than predictive analytics.
How to Ensure Equipment Calibration
Fortunately, businesses can ensure the continued quality of their data-collecting processes by committing to regular equipment calibration.
While not all industries are subject to equipment calibration regulations, standards from other industries — like those established by the FDA — could provide useful best practice frameworks.
Businesses that don’t have a dedicated equipment maintenance team can choose an external calibration solution or hire or train a team to handle equipment calibration. Some businesses — such as manufacturers who work with numerous advanced or highly sensitive machines — might need multiple calibration teams or companies with specialized experience.
In general, businesses and manufacturers should establish a regular calibration and inspection schedule. Each time someone calibrates a piece of equipment, they should document that process. Documentation should include the date of the last calibration, the results of any tests conducted and the due date for the next calibration. This process can help establish a pattern of sensor error that equipment maintenance teams can use to better predict and respond to glitches.
Even if a business only uses a certain kind of data from one sensor on a piece of testing equipment, workers should test every sensor on that machine. Errors from other sensors can influence properly calibrated sensors, even if no one is actively using the data they collect. This will become even truer as smart analysis technologies and IoT platforms become more common and algorithms handle larger portions of the data analysis process.
Calibrating Equipment for Accurate Data
Data is one of the most valuable resources available to modern businesses. However, a cost comes with relying too heavily on data and not properly calibrating the equipment that collects that data.
Equipment calibration is key to maintaining data integrity. If testing equipment and sensors aren’t properly calibrated, they can record incorrect data, which may lead to delays or lower product quality. Regular equipment calibration can help businesses ensure the data they receive is accurate and of the highest caliber.


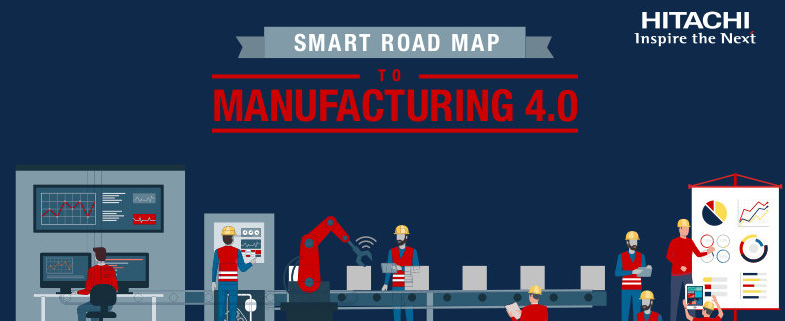
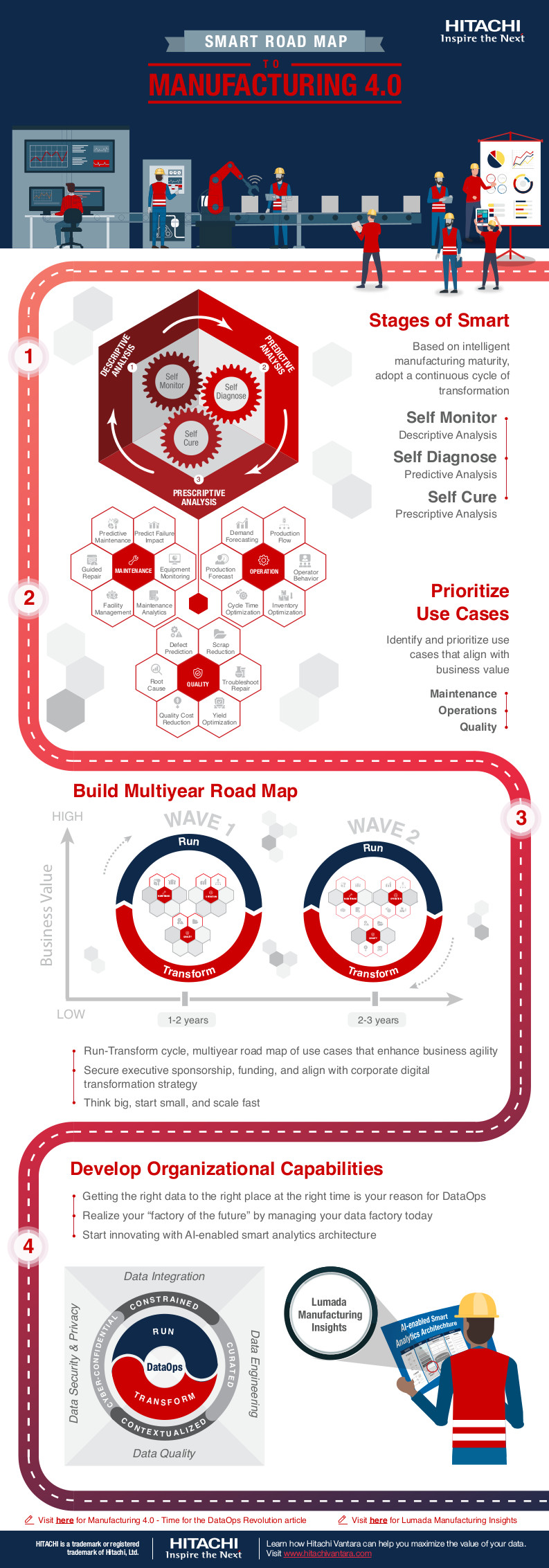

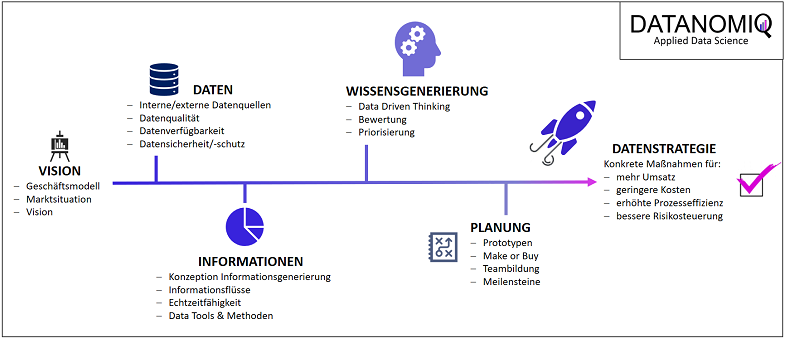
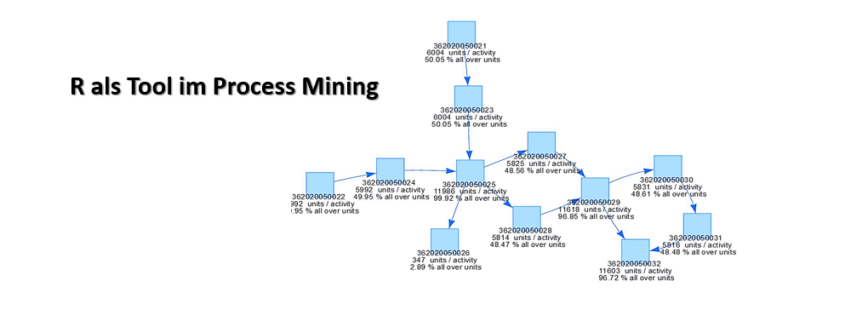
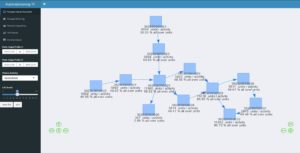
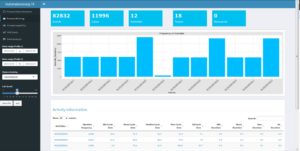
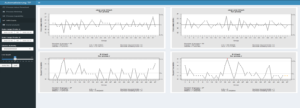
 Mein Vortrag zur Datenstrategie am Data Leader Day 2017
Mein Vortrag zur Datenstrategie am Data Leader Day 2017